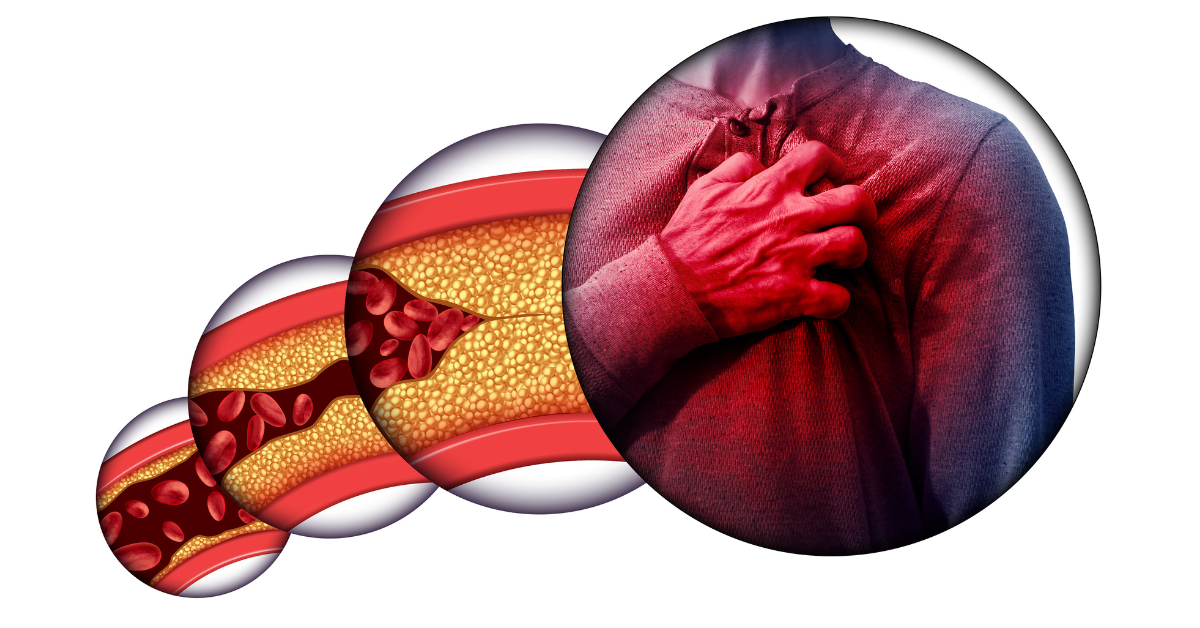
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a major concern worldwide, including in Singapore and Malaysia. The condition occurs when plaque (fatty deposits of cholesterol and other substances) builds up inside the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. Without timely care, this may lead to angina, heart attacks, or even sudden cardiac death.
The good news is that advances in coronary heart disease treatment now allow patients to detect the condition early, manage symptoms effectively, and significantly reduce the risk of complications. In this guide, we will cover the main diagnostic methods and treatment options available in Singapore and Malaysia.
Back to Main Channel: Angiography and Stent Placement for the Heart
Explore CT Angiogram Packages at our Mall
How Coronary Heart Disease is Diagnosed
Before starting any coronary heart disease treatment, accurate diagnosis is essential. Doctors use a combination of advanced imaging tests and physical examinations to evaluate the severity of blockages and plan the best approach.
CT Angiogram (Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography)
A CT Angiogram is a highly effective non-invasive diagnostic tool for coronary heart disease. It uses advanced CT imaging and contrast dye to produce detailed pictures of the coronary arteries, helping to identify narrowing or blockages. This test is commonly recommended for patients with chest discomfort, shortness of breath, or multiple cardiovascular risk factors.
Coronary Angiography
Coronary angiography is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure performed in a hospital setting. A thin catheter is inserted through the wrist or groin and guided to the coronary arteries. Contrast dye is injected, and X-ray images are taken to show the precise location and severity of blockages. If significant narrowing is found, treatment such as angioplasty may be performed during the same session.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An ECG records the heart’s electrical activity. It can show evidence of previous heart attacks, ongoing damage, or irregular rhythms, making it an important first step in identifying coronary heart disease.
Stress Test
A stress test measures how the heart performs under physical exertion. It can reveal reduced blood supply to the heart, which may indicate narrowing of the arteries that require treatment.
Echocardiogram
This ultrasound scan allows doctors to see how the heart muscle is functioning and whether it has been affected by coronary heart disease. It is especially useful in assessing complications such as weakened heart pumping ability.
Coronary Heart Disease Treatment Options
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment will be tailored to the patient’s condition. Options include lifestyle changes, medication, and interventional procedures such as angioplasty and stent placement.
Coronary Angioplasty and Stent Placement
One of the most common forms of coronary heart disease treatment is angioplasty with stent placement. In this procedure, a small balloon is used to open narrowed arteries, followed by the placement of a stent to keep the artery open. Stents may also be drug-eluting, releasing medication to prevent further narrowing. This procedure restores blood flow, relieves chest pain, and reduces the risk of future heart attacks.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
CABG, commonly known as bypass surgery, is a surgical treatment option for patients with severe coronary artery disease, multiple blockages, or cases where angioplasty is not suitable. In this procedure, a surgeon uses a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body (such as the leg or chest) to create a new route for blood to flow around the blocked arteries. CABG improves blood supply to the heart muscle, relieves angina, and reduces the risk of future cardiac events.
Medications
Patients with coronary heart disease are often prescribed:
- Statins to reduce cholesterol.
- Blood thinners to prevent clot formation.
- Beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers to control blood pressure and heart rate.
- ACE inhibitors to protect and support heart function.
Lifestyle Management
Even with medical intervention, lifestyle plays a major role in treatment. Patients are advised to quit smoking, adopt a heart-healthy diet, maintain an active lifestyle, reduce stress, and keep blood pressure and diabetes under control. These steps can complement medical therapy and prevent further complications.
Accessing Coronary Heart Disease Treatment in Singapore and Malaysia
Explore CT Angiogram Packages in Singapore and Malaysia
Detect heart disease before symptoms become severe.

Get connected with experienced Cardiologists
Receive personalised care and treatment recommendations tailored to your needs.
For inquiries, contact us below
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most common coronary heart disease treatment?
Angioplasty with stent placement is one of the most common treatments for blocked coronary arteries. Medications and lifestyle changes are also essential parts of treatment.
2. When should I consider a CT Angiogram?
If you have symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath, or if you have risk factors such as diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, or a family history of heart disease, a CT Angiogram is highly recommended.
3. What is the difference between CT Angiogram and coronary angiography?
A CT Angiogram is non-invasive, while a coronary angiography is invasive but can be combined with immediate treatment such as angioplasty if needed.
4. Can coronary heart disease treatment cure the condition completely?
While coronary heart disease cannot be cured permanently, effective treatment and lifestyle changes can control the disease, improve quality of life, and reduce the risk of complications.
5. Is coronary heart disease treatment available in both Singapore and Malaysia?
Yes. Both countries have advanced cardiology centres that offer CT Angiograms, angioplasty, stent placement, and medication management for coronary heart disease.
Useful Links
Related Content
- Angiography and Stent Placement for the Heart
- Medical Imaging – See Clearly, Diagnose Early
- CT Angiogram
- Complete Guide To Coronary Angioplasty
Disclaimer: 365Asia aims to provide accurate and up-to-date information, our contents do not constitute medical or any professional advice. If medical advice is required, please consult a licensed healthcare professional. Patient stories are for general reading. They are based on third-party information and have not been independently verified.