A thyroid lump, also known as a thyroid nodule, is a growth or swelling in the thyroid gland located at the front of the neck. While most thyroid lumps are benign, some may indicate underlying conditions such as thyroid cancer, hyperthyroidism, or cysts. Understanding the available treatment options, including surgical and non-surgical alternatives, is crucial for effective management and peace of mind.
Back to Big Story: Thyroid Surgery
Schedule an Appointment with a Thyroid Specialist
Understanding Thyroid Lumps
Thyroid lumps are common, particularly in women and older adults. Men are less commonly affected, but thyroid lumps in men have a slightly higher chance of being malignant.
Early assessment is key. Detecting and treating thyroid lumps promptly improves outcomes and allows for personalised care.
Thyroid Lump Treatment Options
1. Active Monitoring
Not all thyroid lumps require immediate intervention. If the nodule is small, non-cancerous, and not causing symptoms, doctors may recommend regular monitoring. This typically includes:
- Thyroid function tests – to assess hormone levels.
- Ultrasound scans – to track any changes in size or structure.
- Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy – if there is any suspicion of malignanc
Monitoring is suitable for benign lumps and ensures that any changes are detected early without undergoing unnecessary procedures.
2. Medication
Some thyroid lumps are linked to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. In such cases, treatment may include:
- Thyroid hormone therapy – to regulate hormone levels.
- Anti-thyroid medications – to reduce thyroid overactivity.
Medication alone cannot remove the lump but may help manage associated symptoms and prevent further growth.
3. Treatments for Benign Nodules
For benign thyroid nodules, minimally invasive treatments can be considered before surgical intervention:
- Needle Aspiration: This treatment may be considered as a first-line therapy for a simple thyroid cyst. It is most suitable for nodules that are completely cystic in nature. Needle aspiration is performed using a small needle at the bedside, with or without the assistance of ultrasound. The fluid that is extracted may be sent for cytology analysis. Recurrence and re-accumulation of the fluid are possible, and repeat aspiration may be performed. Surgical excision should be considered for further recurrence.
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU): HIFU uses therapeutic ultrasound to heat thyroid nodule tissue to around 85°C, effectively “melting” it away. The nodule gradually shrinks as the body absorbs the treated tissue, typically reducing by 60–70% over 6–12 months. This outpatient procedure is performed under local anaesthesia, with or without sedation, and usually takes 20–30 minutes depending on the nodule size. Patients may feel mild pain during the pulse phase, often manageable with sedation. HIFU is a non-invasive, scarless option suitable for patients with benign nodules.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): This minimally invasive technique uses heat energy to shrink nodules. A special needle is introduced into the nodule under ultrasound guidance, delivering heat that gradually reduces the nodule size. The procedure takes around 30 minutes, and patients can typically be discharged shortly after. RFA is ideal for those wishing to avoid surgery while effectively managing benign nodules.
4. Thyroid Surgery
Surgery is often recommended for:
- Suspicious or cancerous nodules.
- Large goitres causing discomfort or difficulty swallowing.
- Nodules unresponsive to other treatments.
Types of thyroid surgery include:
- Hemithyroidectomy – removal of one lobe of the thyroid.
- Total thyroidectomy – removal of the entire thyroid gland.
Surgical treatment is highly effective, especially for malignant or high-risk thyroid lumps, and can be tailored to the patient’s specific condition.
Thyroid Surgeons You May Consider
Thyroid cancer surgery requires precision to ensure complete cancer removal while preserving important structures in the neck, such as the vocal cords and parathyroid glands. Choosing an experienced surgeon can reduce the risk of complications such as hoarseness, low calcium levels, or recurrence.
For inquiries about Thyroid Surgery, surgeons, costs and other information, contact us below.
Screening and Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is critical for optimal outcomes. Common investigations include:
- Thyroid Ultrasound – first-line, non-invasive imaging to examine size, structure, and abnormalities.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy – provides tissue for analysis to determine if a lump is malignant.
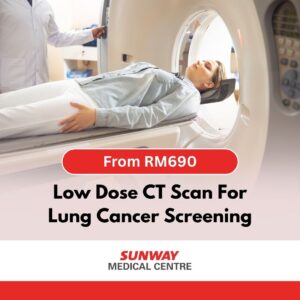
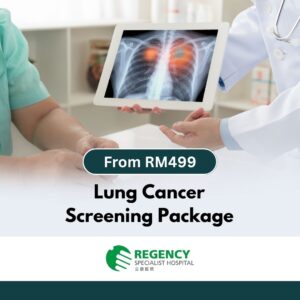
- CT or MRI of the Neck – may be used for further evaluation if there are complex findings.
Medical Imaging Packages You May Consider

Financial Considerations
The cost of thyroid lump treatment can vary depending on the procedure required, the type of hospital (private or public), and the use of additional therapies.
Learn more about costing here: Thyroid Cancer Surgery Cost: What To Expect
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Are thyroid lumps common in Singapore?
Yes, thyroid nodules are fairly common, particularly among women and older adults. Many nodules are benign, but assessment is important to rule out malignancy.
2. Can a thyroid lump be treated without surgery?
Yes, options such as medication, active monitoring, needle aspiration, HIFU, or radiofrequency ablation may be suitable for benign or cystic nodules.
3. How is a thyroid lump diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, thyroid function tests, ultrasound imaging, and sometimes a fine-needle aspiration biopsy.
4. When is thyroid surgery necessary?
Surgery is usually recommended for malignant, suspicious, or large nodules that cause symptoms or do not respond to other treatments.
5. Can thyroid lumps recur after treatment?
Recurrence depends on the type of nodule and treatment. Benign nodules may remain stable, while thorough surgical removal reduces recurrence risk for cancerous nodules.
Disclaimer: 365Asia aims to provide accurate and up-to-date information, our contents do not constitute medical or any professional advice. If medical advice is required, please consult a licensed healthcare professional. Patient stories are for general reading. They are based on third-party information and have not been independently verified.