Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor among women in Malaysia, caused by the uncontrolled growth of cells in the breast that form a lump (tumor). According to the latest report from the Malaysian Ministry of Health and the National Cancer Centre , approximately 4,000 new cases of breast cancer are diagnosed in Malaysia each year, accounting for 34.1% of all female cancer cases, meaning that one in 19 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer.
Age is a significant risk factor for breast cancer, especially for women over 40, whose incidence increases with age.
In Malaysia, Johor Bahru, a major medical center in the south, boasts a large number of experienced breast cancer specialists. From breast lump screening and breast imaging to personalized treatment plans after diagnosis, professional breast surgeons and oncologists can provide comprehensive assistance. This article will guide you through the early signs of breast cancer, common treatments, and recommend several reputable breast cancer specialists in Johor Bahru to help you make more informed choices during your treatment journey.
What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
The most common characteristic of breast cancer is that it often has no obvious symptoms in its early stages. Most breast cancer patients discover a lump in their breast during a physical examination or screening, while a small number discover it through self-examination or by feeling a lump during a doctor’s examination. However, ‘nipple retraction’ and ‘orange peel appearance’ are characteristics of mid-to-late stage breast cancer. Therefore, regular self-examination and screening are the most effective ways to detect breast cancer early and improve survival rates.
When should breast cancer screening be performed?
Generally speaking:
- Women aged 50 and over: According to Malaysian clinical indicators, it is recommended that women aged 50 and over undergo mammogram screening every two years until age 74. These screenings are very effective in detecting breast cancer at an early stage.
- Women aged 40 to 49: For women in this age group, especially those with a family history of breast cancer or other high-risk factors, it is recommended to discuss the appropriateness of screening with your doctor. In some cases, your doctor may recommend starting regular screening.
- High-risk women: If there are high-risk factors such as a family history of breast cancer or hereditary BRCA gene mutations, it is recommended to have a mammogram and MRI scan (magnetic resonance imaging) once a year between the ages of 30 and 39.
Every woman’s risk of breast cancer is different. It is recommended that you discuss a suitable physical examination and screening plan with your doctor based on your own situation to ensure timely detection and treatment of potential breast cancer.
Breast cancer screening methods
- Breast self-examination
Women should perform a breast self-exam once a month. Here is a simple three-step method:
Step 1: Observation
Observe the shape of the breasts, the skin surface, and the nipples for any asymmetry, wrinkling, dimpling, or changes. Raise both arms and observe any changes under the breasts.
Step 2: Touch
Observe the shape of the breasts, the skin surface, and the nipples for any asymmetry, wrinkling, dimpling, or changes. Raise both arms and observe any changes under the breasts.
Step 3: Inspection
Examine the entire breast from the armpit to the cleavage for any lumps, and do the same for the other breast.
- Breast cancer imaging examination
While a small percentage of patients are diagnosed with breast cancer after discovering a lump during a self-examination, this is not the most efficient or accurate method of detection. Breast size, the location and texture of the lump, and the examination technique can all affect the results. Even if no lump is found during a self-examination, the possibility of breast cancer cannot be completely ruled out.
Imaging examinations are the most effective and accurate method for breast cancer screening.
- Mammogram
Mammography is considered one of the most reliable methods for breast cancer screening in Malaysia. Using low-dose X-rays, doctors can examine breast tissue for abnormalities in the images, helping to detect breast cancer at an early stage. There are two main types of mammograms:
i. Two-dimensional mammogram : Provides two-dimensional images of the breast from top to bottom and side views, and is the most commonly used screening method.
ii. 3D Mammogram : Creates a three-dimensional view of the breast by taking images from multiple angles, which helps to distinguish tissue details more clearly and is especially suitable for women with high breast tissue density.
- Breast ultrasound
Breast ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to generate images of breast tissue. It is suitable for women with high breast density and can detect small lumps. It is usually used as a supplement to mammograms to improve diagnostic accuracy. Ultrasound examinations are available in almost all public and private hospitals in Malaysia.
i. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the breast is a highly sensitive imaging examination that uses strong magnetic fields and radiofrequency waves to generate detailed images of the breast. It is generally recommended for high-risk women, such as those with a family history of breast cancer or those carrying BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations. MRI can better visualize the complex structure of the breast, aiding in early diagnosis.
ii. Breast CT scan
Some high-end hospitals and clinics in Malaysia also offer breast CT scans. This method uses X-rays and computer technology to generate three-dimensional images, suitable for patients requiring further examination, and provides detailed structural information. It is often used as a supplementary tool in diagnosis.
iii. Nuclear imaging
For some high-risk patients requiring more in-depth testing, molecular breast imaging (MBI) is a novel diagnostic method. This technique involves injecting a small amount of radioactive tracer, which is then detected by specific imaging equipment to help observe abnormal cell activity in the breast, providing early diagnostic information for breast cancer in certain cases.
These screening tests are available at major public and private hospitals in Malaysia, with costs and subsidy policies varying depending on the hospital and the patient’s circumstances.
💡 For more information about imaging examinations, 👉Click here to read more
2026 Recommended Breast Cancer Doctors in Johor Bahru, Malaysia
| # | Doctor’s Name | Areas of expertise | Affiliation | Academic Qualifications and Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
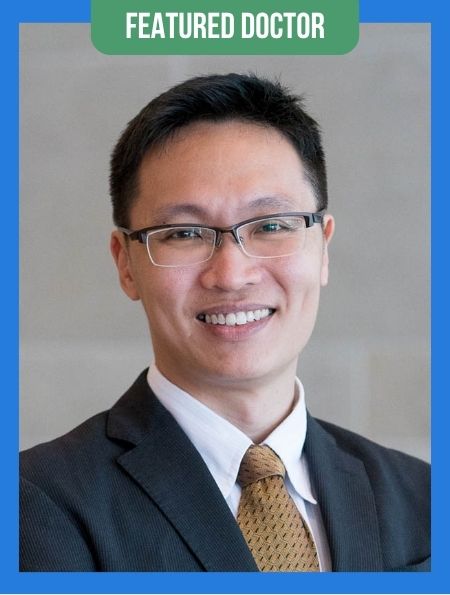
| 1 | Dr. Henry Tan Chor Lip | Early detection and surgical treatment of breast cancer (with particular focus on breast lumps and benign breast diseases). | KPJ Bandar Dato’ Onn Specialist Hospital (Johor Bahru) | MD (UCSI), Doctor General Surgery (UKM), CMIA (NIOSH), AM (Mal) |
| 2 | Dr. Leong Ai Chen | Breast and Endocrine Surgery | Gleneagles Hospital Medini Johor | MD (UNIMAS), MS (General Surgery, UKM), MRCS (Edinburgh), Fellowship Breast and Endocrine Surgery (MOH), Fellow European Board of Surgery, Breast Surgery (FEBS) |
| 3 | Dr. Teo Yin Keong | Clinical Oncology | Gleneagles Hospital Medini Johor | MBBS (MMMC), MMED Clinical Oncology (UM) |
| 4 | Dr. Ting Sing Chuen | Breast surgery and minimally invasive surgery | Regency Specialist Hospital | MD (China Medical College, Taiwan), Specialist in General Surgery (Taiwan), Member of Society of Colon & Rectal Surgeons (Taiwan), Registered Specialist (General Surgery, NSR Malaysia) |
| 5 | Dr. Joan Gan Cheau Yan | Diagnosis and treatment of breast diseases (including breast lumps, breast cancer, and benign breast lesions), breast cancer screening, biopsy and breast-conserving surgery, and minimally invasive surgery. | Regency Specialist Hospital | MD (USM), Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians of the United Kingdom (MRCP, UK) |
Johor Bahru Breast Cancer Specialist Hospital, Malaysia
If you are in Johor Bahru, or considering getting breast cancer screening there, we recommend the following hospitals or clinics. Each hospital or clinic has a professional team and advanced equipment, enabling them to effectively detect and identify breast cancer at an early stage.
Malaysian Breast Cancer Screening Package

Frequently Asked Questions
It is recommended to bring your previous medical examination reports, imaging scans (such as mammograms or ultrasounds), and family medical history information to help doctors comprehensively assess your condition and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Costs vary depending on the treatment method (surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy). A typical mastectomy costs between RM8,000 and RM20,000 , while the total cost, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy, can reach RM30,000 to RM60,000.
Yes. Many hospitals offer female breast surgeons or radiologists as options, and patients can schedule appointments based on their personal comfort and needs.
What are some early symptoms of breast cancer that you should be aware of?
Symptoms may include lumps in the breast or armpit, nipple discharge, dimpled or red skin, and inverted nipples. If any of these symptoms occur, it is recommended to go to the hospital for examination as soon as possible.
Recommended colorectal cancer specialist: Dr. Henry Tan Chor Lip
Contact Us
Health365 collaborates with numerous authoritative local and overseas medical institutions to provide professional and reliable breast health consultations and referrals. If you would like to learn more about breast cancer screening, diagnosis, or treatment options , please feel free to contact us. We will arrange suitable breast specialists and hospitals for you , helping you receive the most appropriate medical care.
Disclaimer: 365Asia aims to provide accurate and up-to-date information, our contents do not constitute medical or any professional advice. If medical advice is required, please consult a licensed healthcare professional. Patient stories are for general reading. They are based on third-party information and have not been independently verified.
















